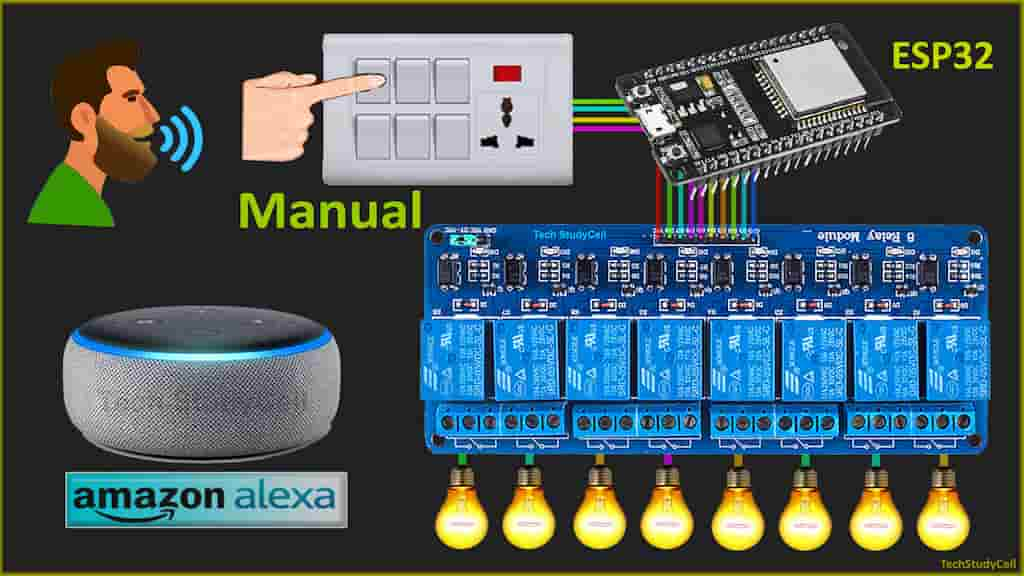
In this ESP32 project, I have explained how to make a smart home system using the ESP32 & Alexa controlled relay module. With this internet of things project, you can control 8 home appliances from the Amazon Alexa App and manual switches. You can control the relay module from the manual switches if there is no internet available.
**This tutorial is outdated. Follow the new tutorial instead: [NEW] ESP32 Home Automation with Alexa & Google Assistant.
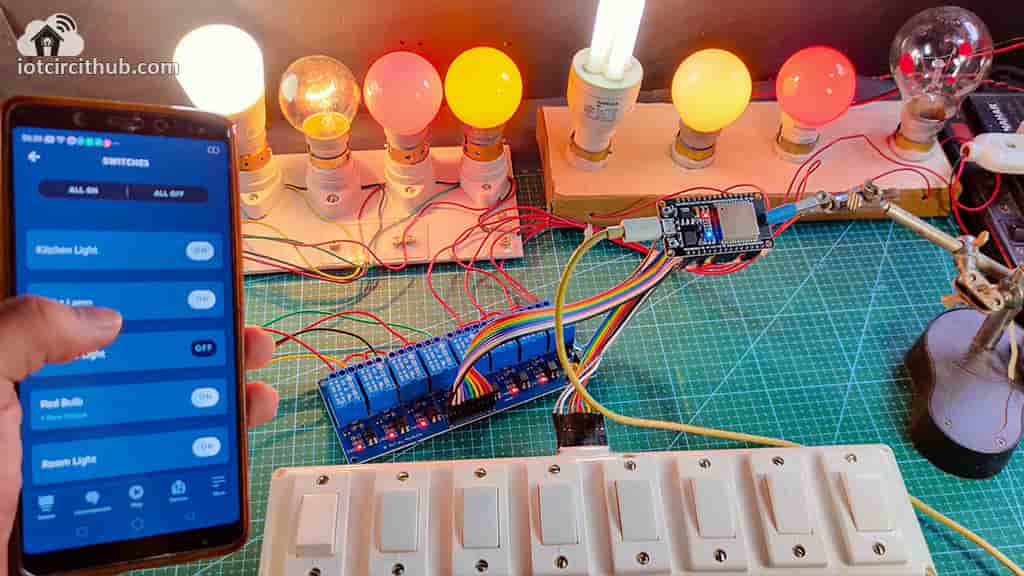
With this IoT project, you can control & monitor the real-time feedback of the relays in the Alexa App from anywhere in the world. You don’t need an Alexa device for this home automation project. If the WiFi is available, the ESP32 will automatically connect with the WiFi and the blue LED will turn on.
Table of Contents
Circuit of the ESP32 Smart Home System
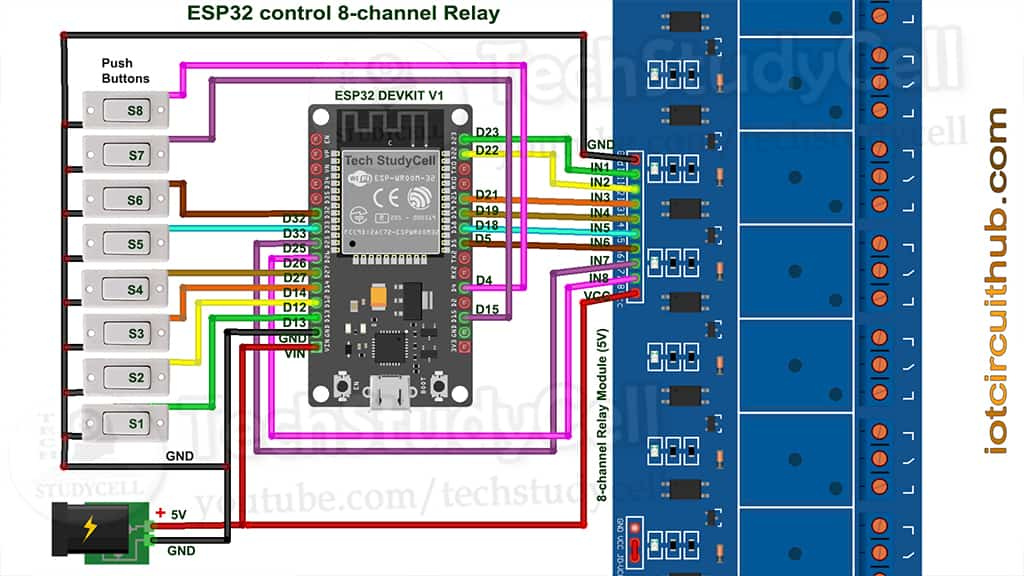
The circuit is very simple, I have used D23, D22, D21, D19, D18, D5, D25 & D26 GPIO to control the 8-channel relay module.
And the GPIO D13, D12, D14, D27, D33, D32, D15 & D4 connected with manual switches to control the relay module manually.
I have used the INPUT_PULLUP function in Arduino IDE instead of using the pull-up resistors with each switch.
As per the source code, when the control pins of the relay module receive the LOW signal the respective relay will turn on and the relay will turn off for the HIGH signal in the control pin.
I have used a 5V 2Amp mobile charger to supply the circuit.
Required Components for the ESP32 projects
- ESP32 DEV KIT V1
- 8-channel 5V SPDT Relay Module
- Manual Switches
- Amazon Echo Dot (optional)
Control Relays with & without WiFi using ESP32

With Internet
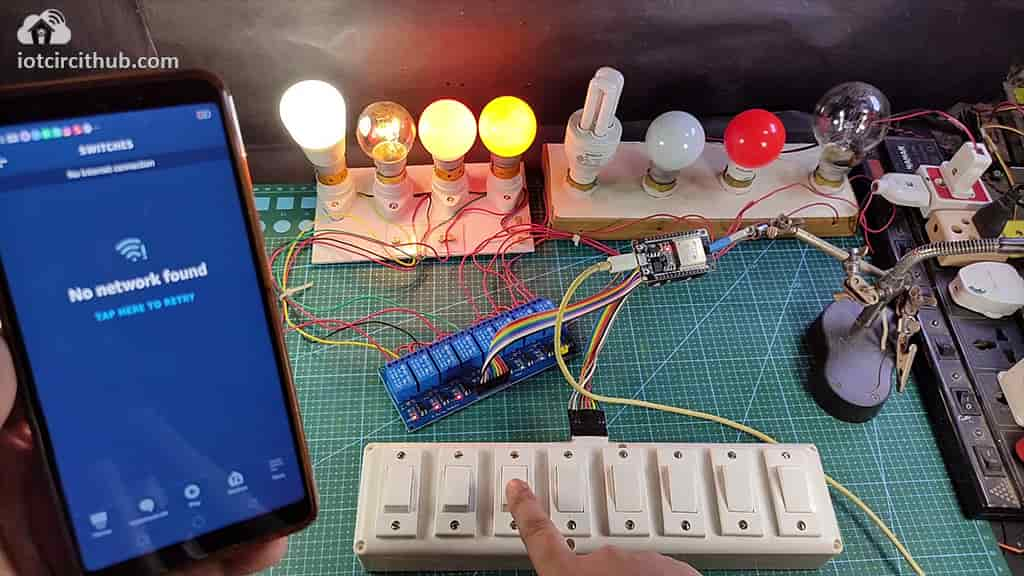
If the ESP32 is connected with WiFi, then you can control the relay module from Amazon Alexa App and manual switches. You can control, monitor the current status of the switches from anywhere in the world from the Alexa App.

Without Internet
If the WiFi not available, you can control the relays from the switches manually.
The ESP32 will check for the WiFi after every 5 seconds. When the internet comes back, the ESP32 will automatically connect with the WiFi.
Tutorial video on ESP32 Alexa Home Automation
In the tutorial video, I have covered the following steps in details.
- Control 8-channel relay module with Alexa and switches.
- Create an account and add devices in Sinric.com.
- Programming the ESP32 with Arduino IDE
- Connect IoT devices & ESP32 with Amazon Alexa App.
- Connect home appliances with the 8-channel relay module.
Create an Account in Sinric.com
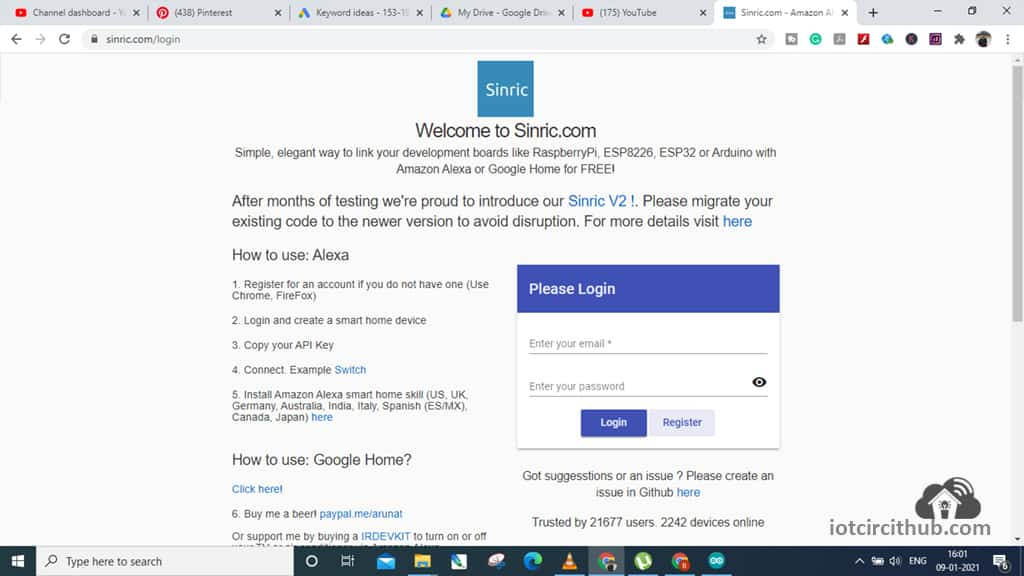
First, visit Sinric.com. Then click in Resistor to create an account.
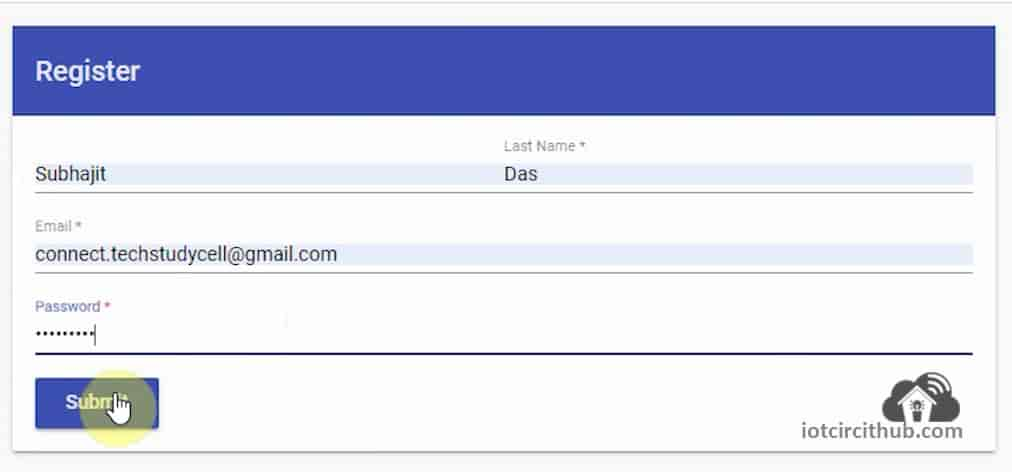
Then enter Name, Email Id and set a password for the Sinric account.
Then click on “Submit“.
Add Devices in Sinric account
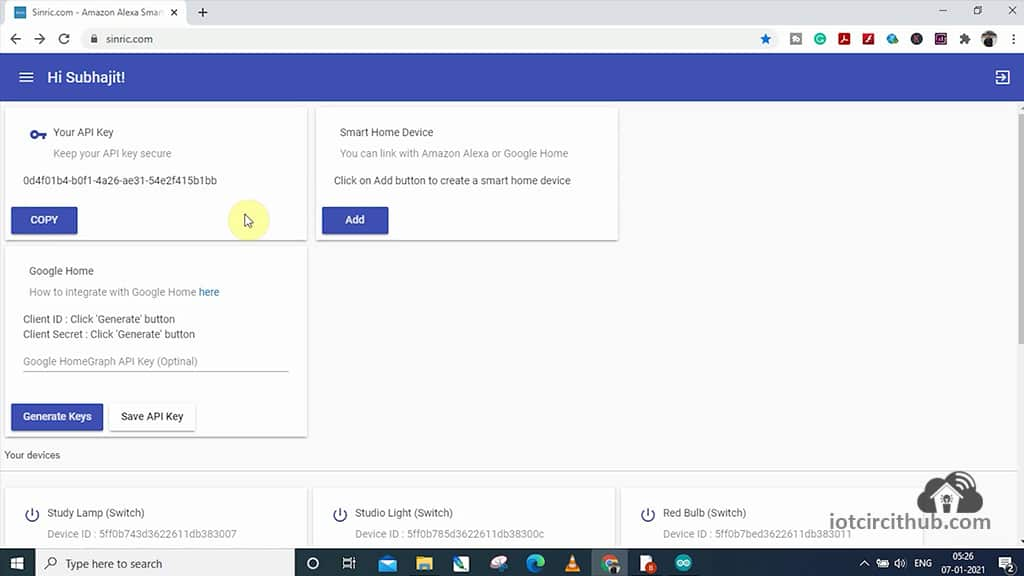
After Login, you will get a API Key which will be required in the code.
Now, to add devices, click on “Add“.
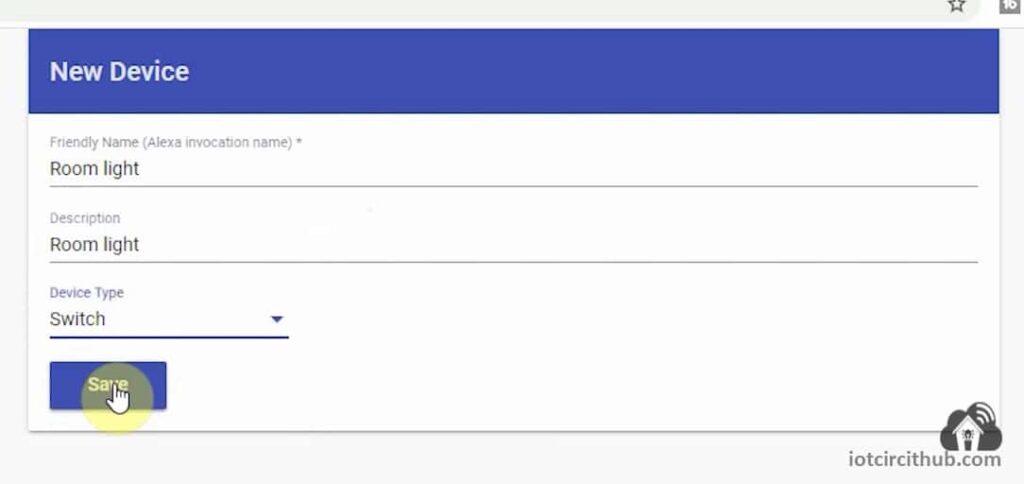
Then, give a Device Name (Alexa will identify the device with this name).
Select the Device Type as “Switch“.
Then click on “Save“.
Thus you can add multiple devices in the Sinric dashboard.
Program ESP32 with Arduino IDE
In the Tutorial video, I have explained all the steps to program the ESP32 DEV KIT V1 using Arduino IDE.
- Update the Preferences –> Aditional boards Manager URLs: https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json, http://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json
- Then install the ESP32 board from the Board manager or Click Here to download the ESP32 board.
- Download the required libraries from the following links:
- arduinoWebSockets Library: Click Here
- AceButton Library: Click Here
- ArduinoJson Library: Click Here
**Please download the latest version of the libraries from the given links. Then install the libraries at Arduino IDE – Sketch – Include Library – Add Zip Library.
Code for ESP32 Alexa controlled relay
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <WiFiMulti.h>
#include <WebSocketsClient.h>
#include <ArduinoJson.h>
#include <StreamString.h>
#include <AceButton.h>
using namespace ace_button;
WiFiMulti WiFiMulti;
WebSocketsClient webSocket;
WiFiClient client;
#define MyApiKey "----------------" // TODO: Change to your sinric API Key. Your API Key is displayed on sinric.com dashboard
#define MySSID "--------" // TODO: Change to your Wifi network SSID
#define MyWifiPassword "------" // TODO: Change to your Wifi network password
#define HEARTBEAT_INTERVAL 300000 // 5 Minutes
uint64_t heartbeatTimestamp = 0;
bool isConnected = false;
String device_ID_1 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_2 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_3 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_4 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_5 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_6 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_7 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_8 = "------------------------";
// define the GPIO connected with Relays and switches
//Relays
#define RelayPin1 23 //D23
#define RelayPin2 22 //D22
#define RelayPin3 21 //D21
#define RelayPin4 19 //D19
#define RelayPin5 18 //D18
#define RelayPin6 5 //D5
#define RelayPin7 25 //D25
#define RelayPin8 26 //D26
// Switches
#define SwitchPin1 13 //D13
#define SwitchPin2 12 //D12
#define SwitchPin3 14 //D14
#define SwitchPin4 27 //D27
#define SwitchPin5 33 //D33
#define SwitchPin6 32 //D32
#define SwitchPin7 15 //D15
#define SwitchPin8 4 //D4
//WiFi Status LED
#define wifiLed 2 //D2
ButtonConfig config1;
AceButton button1(&config1);
ButtonConfig config2;
AceButton button2(&config2);
ButtonConfig config3;
AceButton button3(&config3);
ButtonConfig config4;
AceButton button4(&config4);
ButtonConfig config5;
AceButton button5(&config5);
ButtonConfig config6;
AceButton button6(&config6);
ButtonConfig config7;
AceButton button7(&config7);
ButtonConfig config8;
AceButton button8(&config8);
void handleEvent1(AceButton*, uint8_t, uint8_t);
void handleEvent2(AceButton*, uint8_t, uint8_t);
void handleEvent3(AceButton*, uint8_t, uint8_t);
void handleEvent4(AceButton*, uint8_t, uint8_t);
void handleEvent5(AceButton*, uint8_t, uint8_t);
void handleEvent6(AceButton*, uint8_t, uint8_t);
void handleEvent7(AceButton*, uint8_t, uint8_t);
void handleEvent8(AceButton*, uint8_t, uint8_t);
void setPowerStateOnServer(String deviceId, String value);
// deviceId is the ID assgined to your smart-home-device in sinric.com dashboard. Copy it from dashboard and paste it here
void turnOn(String deviceId) {
if (deviceId == device_ID_1) // Device ID of 1st device
{
Serial.print("Turn on device id: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin1, LOW);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_2) // Device ID of 2nd device
{
Serial.print("Turn on device id: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin2, LOW);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_3) // Device ID of 3rd device
{
Serial.print("Turn on device id: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin3, LOW);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_4) // Device ID of 4th device
{
Serial.print("Turn on device id: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin4, LOW);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_5) // Device ID of 5th device
{
Serial.print("Turn on device id: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin5, LOW);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_6) // Device ID of 6th device
{
Serial.print("Turn on device id: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin6, LOW);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_7) // Device ID of 7th device
{
Serial.print("Turn on device id: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin7, LOW);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_8) // Device ID of 8th device
{
Serial.print("Turn on device id: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin8, LOW);
}
}
void turnOff(String deviceId) {
if (deviceId == device_ID_1) // Device ID of 1st device
{
Serial.print("Turn off Device ID: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin1, HIGH);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_2) // Device ID of 2nd device
{
Serial.print("Turn off Device ID: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin2, HIGH);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_3) // Device ID of 3rd device
{
Serial.print("Turn off Device ID: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin3, HIGH);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_4) // Device ID of 4th device
{
Serial.print("Turn off Device ID: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin4, HIGH);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_5) // Device ID of 5th device
{
Serial.print("Turn off Device ID: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin5, HIGH);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_6) // Device ID of 6th device
{
Serial.print("Turn off Device ID: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin6, HIGH);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_7) // Device ID of 7th device
{
Serial.print("Turn off Device ID: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin7, HIGH);
}
if (deviceId == device_ID_8) // Device ID of 8th device
{
Serial.print("Turn off Device ID: ");
Serial.println(deviceId);
digitalWrite(RelayPin8, HIGH);
}
}
void webSocketEvent(WStype_t type, uint8_t * payload, size_t length) {
switch (type) {
case WStype_DISCONNECTED:
isConnected = false;
WiFiMulti.addAP(MySSID, MyWifiPassword);
Serial.printf("[WSc] Webservice disconnected from sinric.com!\n");
break;
case WStype_CONNECTED: {
isConnected = true;
Serial.printf("[WSc] Service connected to sinric.com at url: %s\n", payload);
Serial.printf("Waiting for commands from sinric.com ...\n");
}
break;
case WStype_TEXT: {
Serial.printf("[WSc] get text: %s\n", payload);
#if ARDUINOJSON_VERSION_MAJOR == 5
DynamicJsonBuffer jsonBuffer;
JsonObject& json = jsonBuffer.parseObject((char*)payload);
#endif
#if ARDUINOJSON_VERSION_MAJOR == 6
DynamicJsonDocument json(1024);
deserializeJson(json, (char*) payload);
#endif
String deviceId = json ["deviceId"];
String action = json ["action"];
if (action == "setPowerState") { // Switch or Light
String value = json ["value"];
if (value == "ON") {
turnOn(deviceId);
} else {
turnOff(deviceId);
}
}
else if (action == "test") {
Serial.println("[WSc] received test command from sinric.com");
}
}
break;
case WStype_BIN:
Serial.printf("[WSc] get binary length: %u\n", length);
break;
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
WiFiMulti.addAP(MySSID, MyWifiPassword);
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to Wifi: ");
Serial.println(MySSID);
// Waiting for Wifi connect
if (WiFiMulti.run() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print("Connecting...");
}
if (WiFiMulti.run() == WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("WiFi connected. ");
Serial.print("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
}
pinMode(SwitchPin1, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(SwitchPin2, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(SwitchPin3, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(SwitchPin4, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(SwitchPin5, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(SwitchPin6, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(SwitchPin7, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(SwitchPin8, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(RelayPin1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RelayPin2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RelayPin3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RelayPin4, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RelayPin5, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RelayPin6, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RelayPin7, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RelayPin8, OUTPUT);
pinMode(wifiLed, OUTPUT);
//During Starting all Relays should TURN OFF
digitalWrite(RelayPin1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RelayPin2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RelayPin3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RelayPin4, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RelayPin5, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RelayPin6, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RelayPin7, HIGH);
digitalWrite(RelayPin8, HIGH);
//During Starting WiFi LED should TURN OFF
digitalWrite(wifiLed, LOW);
config1.setEventHandler(button1Handler);
config2.setEventHandler(button2Handler);
config3.setEventHandler(button3Handler);
config4.setEventHandler(button4Handler);
config5.setEventHandler(button5Handler);
config6.setEventHandler(button6Handler);
config7.setEventHandler(button7Handler);
config8.setEventHandler(button8Handler);
button1.init(SwitchPin1);
button2.init(SwitchPin2);
button3.init(SwitchPin3);
button4.init(SwitchPin4);
button5.init(SwitchPin5);
button6.init(SwitchPin6);
button7.init(SwitchPin7);
button8.init(SwitchPin8);
// server address, port and URL
webSocket.begin("iot.sinric.com", 80, "/");
// event handler
webSocket.onEvent(webSocketEvent);
webSocket.setAuthorization("apikey", MyApiKey);
// try again every 5000ms if connection has failed
webSocket.setReconnectInterval(5000); // If you see 'class WebSocketsClient' has no member named 'setReconnectInterval' error update arduinoWebSockets
}
void loop() {
if (WiFiMulti.run() != WL_CONNECTED)
{
Serial.println("Not Connected");
digitalWrite(wifiLed, LOW);
}
else
{
Serial.println(" Connected");
digitalWrite(wifiLed, HIGH);
webSocket.loop();
}
button1.check();
button2.check();
button3.check();
button4.check();
button5.check();
button6.check();
button7.check();
button8.check();
if (isConnected) {
uint64_t now = millis();
// Send heartbeat in order to avoid disconnections during ISP resetting IPs over night. Thanks @MacSass
if ((now - heartbeatTimestamp) > HEARTBEAT_INTERVAL) {
heartbeatTimestamp = now;
webSocket.sendTXT("H");
}
}
}
void setPowerStateOnServer(String deviceId, String value) {
#if ARDUINOJSON_VERSION_MAJOR == 5
DynamicJsonBuffer jsonBuffer;
JsonObject& root = jsonBuffer.createObject();
#endif
#if ARDUINOJSON_VERSION_MAJOR == 6
DynamicJsonDocument root(1024);
#endif
root["deviceId"] = deviceId;
root["action"] = "setPowerState";
root["value"] = value;
StreamString databuf;
#if ARDUINOJSON_VERSION_MAJOR == 5
root.printTo(databuf);
#endif
#if ARDUINOJSON_VERSION_MAJOR == 6
serializeJson(root, databuf);
#endif
webSocket.sendTXT(databuf);
}
void button1Handler(AceButton* button, uint8_t eventType, uint8_t buttonState) {
Serial.println("EVENT1");
switch (eventType) {
case AceButton::kEventPressed:
Serial.println("kEventPressed");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_1, "ON");
digitalWrite(RelayPin1, LOW);
break;
case AceButton::kEventReleased:
Serial.println("kEventReleased");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_1, "OFF");
digitalWrite(RelayPin1, HIGH);
break;
}
}
void button2Handler(AceButton* button, uint8_t eventType, uint8_t buttonState) {
Serial.println("EVENT2");
switch (eventType) {
case AceButton::kEventPressed:
Serial.println("kEventPressed");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_2, "ON");
digitalWrite(RelayPin2, LOW);
break;
case AceButton::kEventReleased:
Serial.println("kEventReleased");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_2, "OFF");
digitalWrite(RelayPin2, HIGH);
break;
}
}
void button3Handler(AceButton* button, uint8_t eventType, uint8_t buttonState) {
Serial.println("EVENT3");
switch (eventType) {
case AceButton::kEventPressed:
Serial.println("kEventPressed");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_3, "ON");
digitalWrite(RelayPin3, LOW);
break;
case AceButton::kEventReleased:
Serial.println("kEventReleased");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_3, "OFF");
digitalWrite(RelayPin3, HIGH);
break;
}
}
void button4Handler(AceButton* button, uint8_t eventType, uint8_t buttonState) {
Serial.println("EVENT4");
switch (eventType) {
case AceButton::kEventPressed:
Serial.println("kEventPressed");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_4, "ON");
digitalWrite(RelayPin4, LOW);
break;
case AceButton::kEventReleased:
Serial.println("kEventReleased");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_4, "OFF");
digitalWrite(RelayPin4, HIGH);
break;
}
}
void button5Handler(AceButton* button, uint8_t eventType, uint8_t buttonState) {
Serial.println("EVENT5");
switch (eventType) {
case AceButton::kEventPressed:
Serial.println("kEventPressed");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_5, "ON");
digitalWrite(RelayPin5, LOW);
break;
case AceButton::kEventReleased:
Serial.println("kEventReleased");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_5, "OFF");
digitalWrite(RelayPin5, HIGH);
break;
}
}
void button6Handler(AceButton* button, uint8_t eventType, uint8_t buttonState) {
Serial.println("EVENT6");
switch (eventType) {
case AceButton::kEventPressed:
Serial.println("kEventPressed");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_6, "ON");
digitalWrite(RelayPin6, LOW);
break;
case AceButton::kEventReleased:
Serial.println("kEventReleased");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_6, "OFF");
digitalWrite(RelayPin6, HIGH);
break;
}
}
void button7Handler(AceButton* button, uint8_t eventType, uint8_t buttonState) {
Serial.println("EVENT7");
switch (eventType) {
case AceButton::kEventPressed:
Serial.println("kEventPressed");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_7, "ON");
digitalWrite(RelayPin7, LOW);
break;
case AceButton::kEventReleased:
Serial.println("kEventReleased");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_7, "OFF");
digitalWrite(RelayPin7, HIGH);
break;
}
}
void button8Handler(AceButton* button, uint8_t eventType, uint8_t buttonState) {
Serial.println("EVENT8");
switch (eventType) {
case AceButton::kEventPressed:
Serial.println("kEventPressed");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_8, "ON");
digitalWrite(RelayPin8, LOW);
break;
case AceButton::kEventReleased:
Serial.println("kEventReleased");
setPowerStateOnServer(device_ID_8, "OFF");
digitalWrite(RelayPin8, HIGH);
break;
}
}Enter the following WiFi credential and the Sinric API Key in the code:
#define MyApiKey "----------------"
#define MySSID "--------"
#define MyWifiPassword "---------" - API Key from the Sinric at “MyApiKey“
- WiFi Name at “MySSID“
- WiFi Password at “MyWifiPassword”
String device_ID_1 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_2 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_3 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_4 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_5 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_6 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_7 = "------------------------";
String device_ID_8 = "------------------------";Enter Device ID for each device from the Sinric dashboard.
Then Goto Tools and select the board as “DOIT ESP32 DEVKIT V1” and the proper PORT in Arduino IDE.
Then click on the upload button to program the ESP32 board.
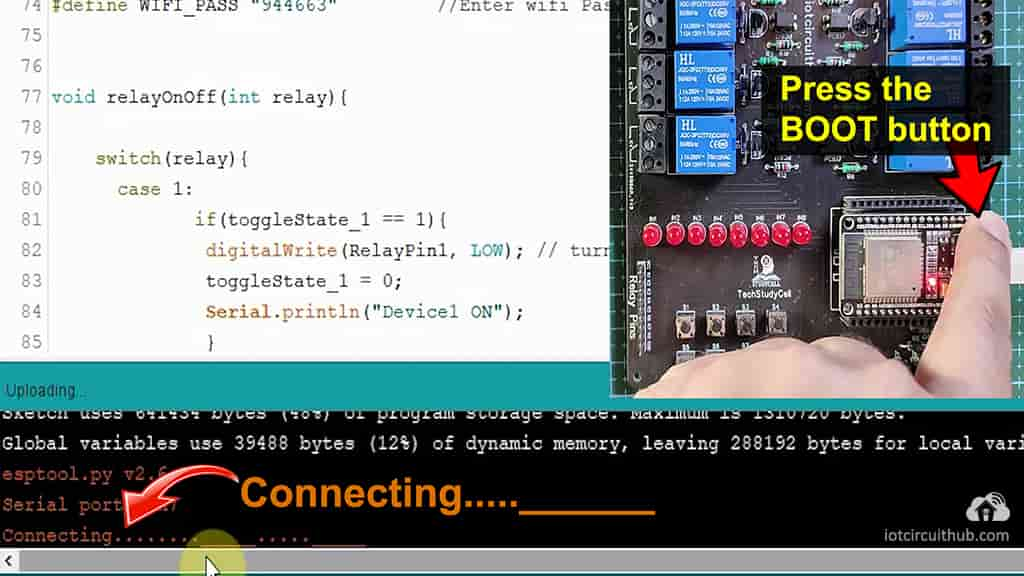
While uploading the code to ESP32, when you see the “Connecting….___” text, then press the BOOT button of the ESP32.
Configure the Amazon Alexa App
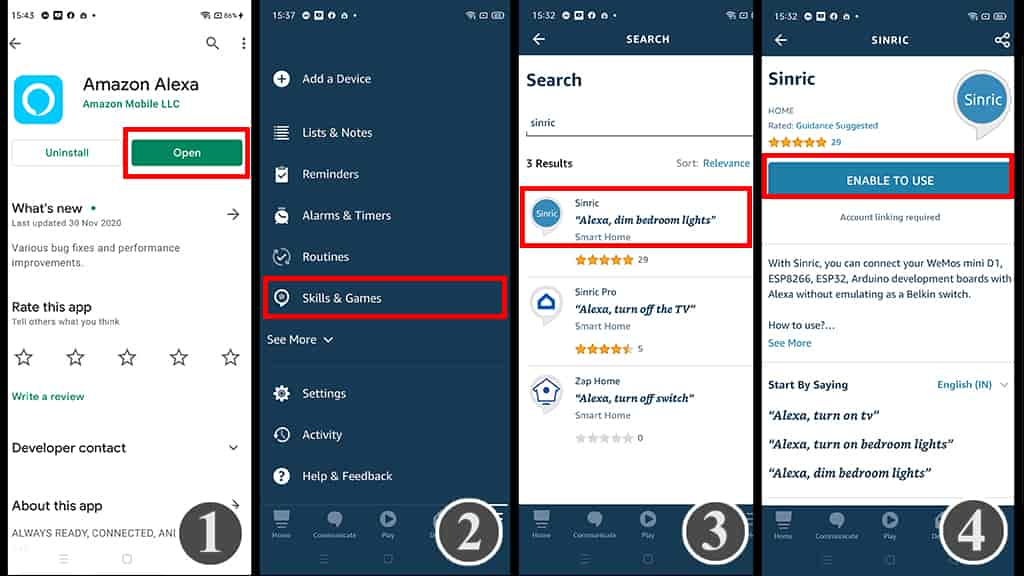
- Download the Amazon Alexa App from Google Play Store or App Store
- Goto More, then select “Skills & Games“
- Search for Sinric and tap on “Sinric“.
- Tap on “ENABLE TO USE“
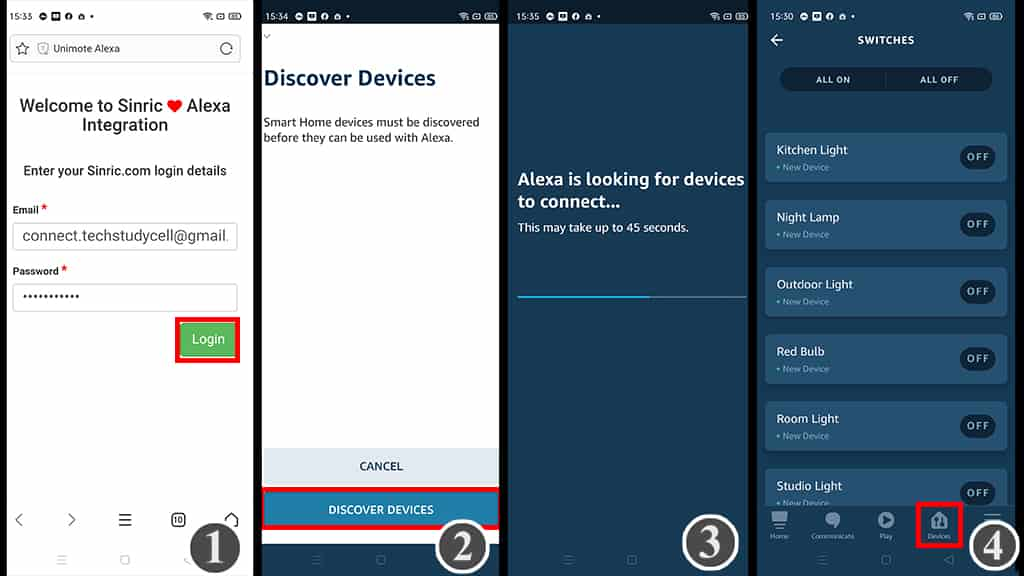
- Log in with the Sinric account credentials.
- Goto Alexa and tap on “DISCOVER DEVICES“.
- It takes a minute to add devices. During this time the ESP32 should be connected with WiFi.
- Tap on “Devices“, then tap on “Switch” to see all the devices.
Now, you can control the connected home appliances with Alexa.
PCB for the Alexa ESP32 Projects
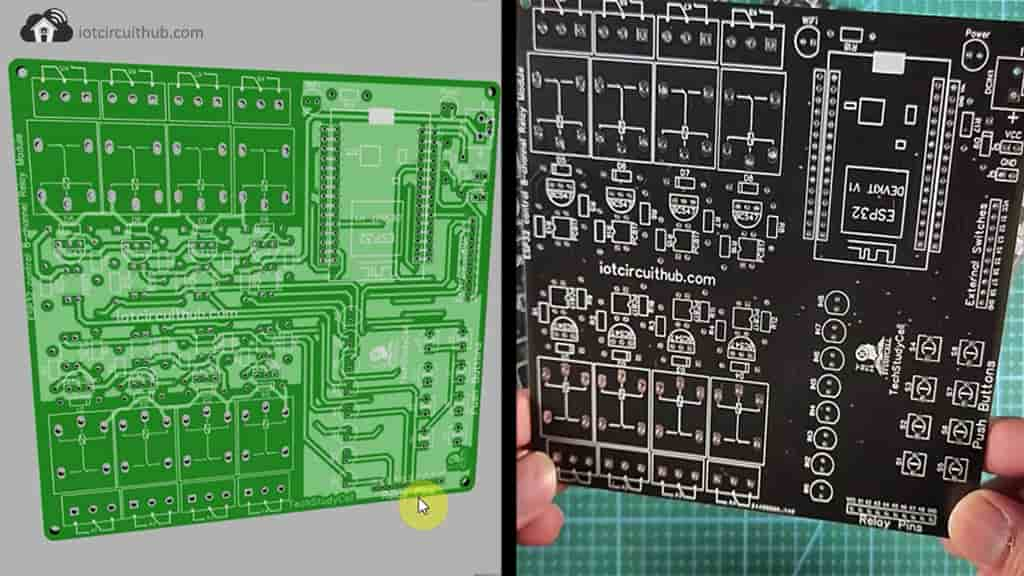
To give the project a professional look and make the circuit compact, I have designed a PCB for this ESP32 home automation project.
Solder the Components on PCB
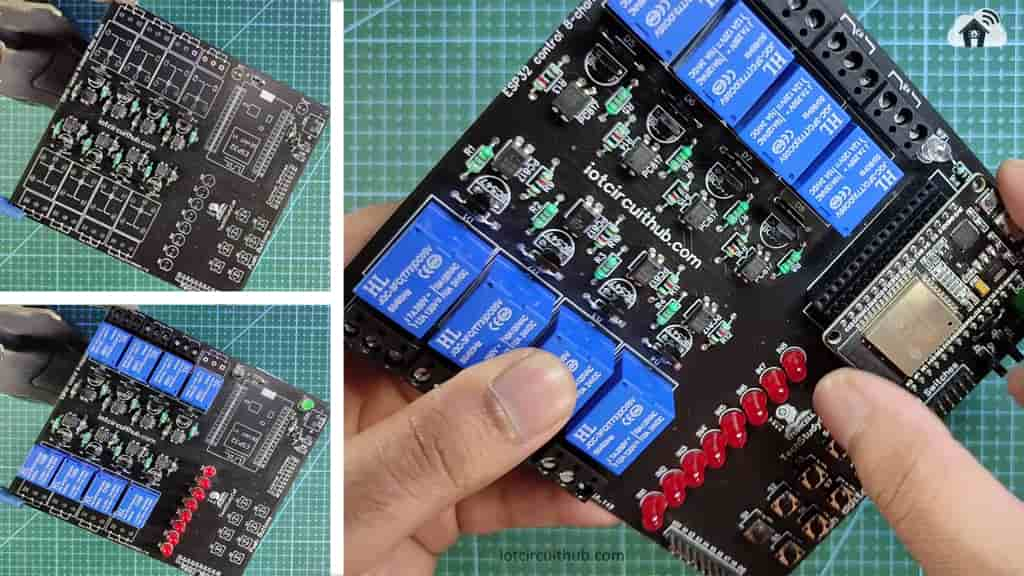
Solder all the components as mentioned on the PCB.
Components Required for PCB
- Relays 5v (SPDT) (8 no)
- BC547 Transistors (8 no)
- PC817 Optocuplors (8 no)
- 510-ohm 0.25-watt Resistor (8 no) (R1-R8)
- 1k 0.25-watt Resistors (10 no) (R9-R18)
- 1N4007 Diodes (8 no) (D1-D8)
- LED 5-mm (10 no)
- Push Buttons (8 no)
- Terminal Connectors
- 5V DC supply
Connect Home Appliances with Relays
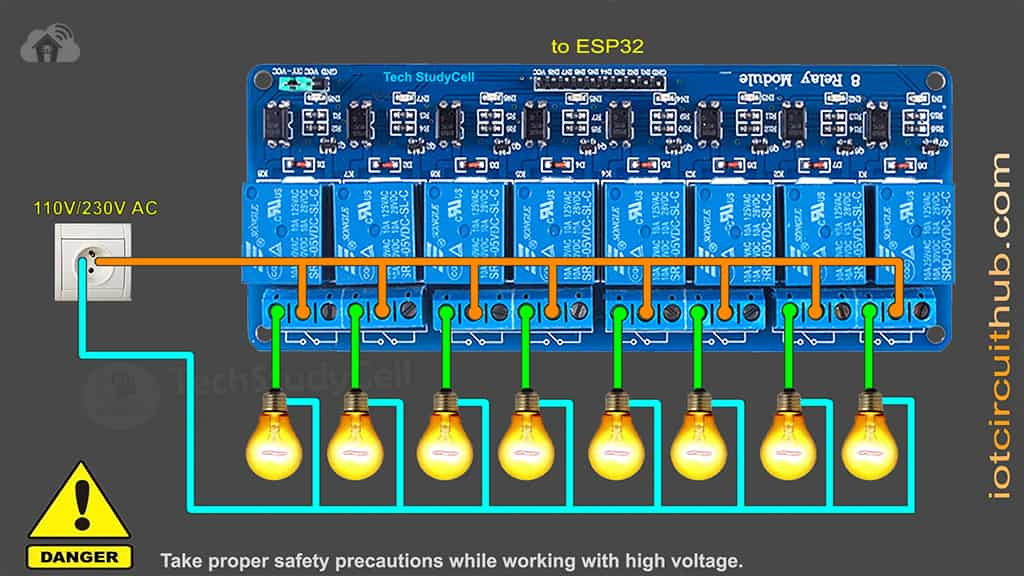
Connect the home appliances with the relay module as per the circuit diagram.
Please take proper safety precaution, while working with high voltage.
Now, turn on the 5V DC supply and 110V/220V AC supply.
Finally, the ESP32 Smart Home System is ready
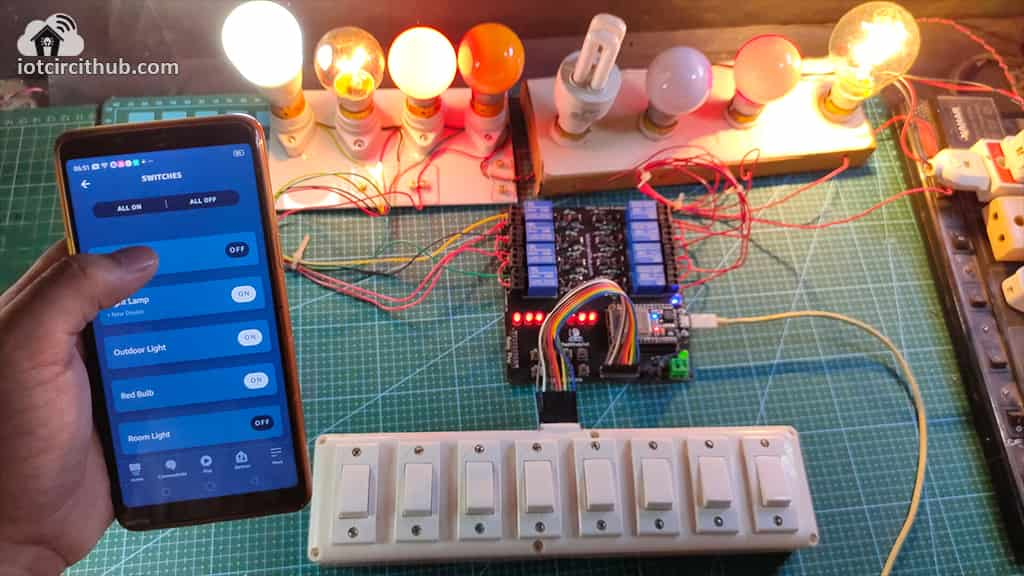

Now, you can control all the 8 home appliances from the Alexa app and also monitor real-time feedback from anywhere in the world.
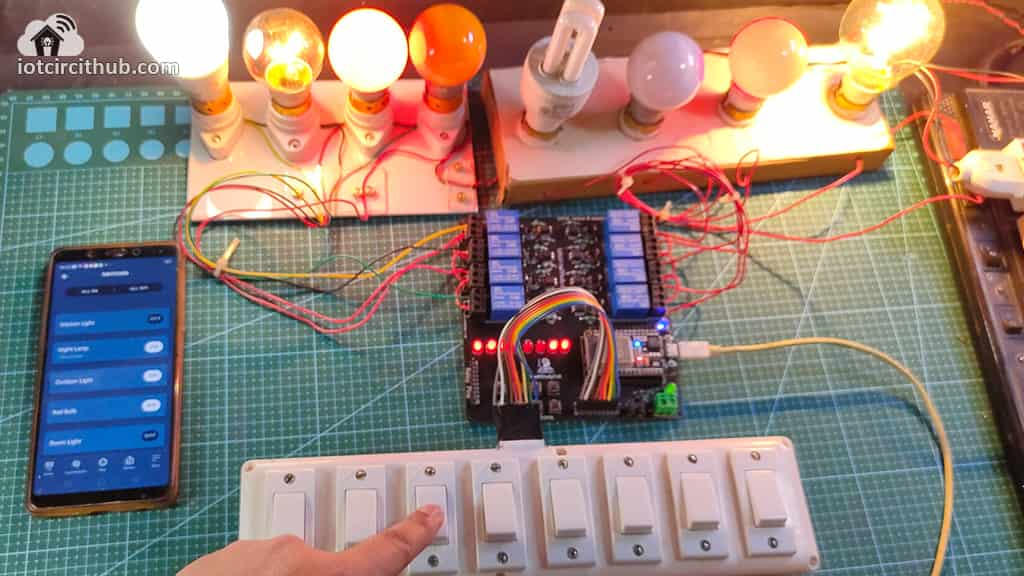
I hope you like this Smart house IoT projects idea with the ESP32 and Alexa app.
Click Here for more such ESP32 projects.
Please do share your feedback on this IoT project. Thank you for your time.