In this beginner’s guide, you will learn step by step how to install Tasmota on ESP8266 device, configure WiFi, and access the Tasmota web interface. No prior programming experience is required.
Table of Contents
What Is Tasmota?
Tasmota is a lightweight firmware designed for ESP8266 and ESP32 devices. It replaces the default firmware and turns your board into a fully configurable smart device that can be controlled locally or integrated with platforms like Amazon Alexa, Google Home, and Home Assistant.
Why Tasmota Is Beginner-Friendly?
✅ No coding required
✅ 100% free and open source
✅ Works locally (no mandatory cloud)
✅ Web-based configuration
✅ Supports relays, LEDs, sensors, switches, and more
What You Need Before Installing Tasmota?
Hardware Required
ESP8266 board (NodeMCU, ESP-12, ESP-01, etc.)
USB cable (data cable, not charging only)
PC or laptop (Windows, macOS, or Linux)
Software / Tools
Tasmotizer software
Tasmota .bin firmware file
Web browser (Chrome, Edge, or Firefox)
Internet connection (for initial setup)
Steps to Install Tasmota on ESP8266
Step 1: Download the required files to flash ESP8266
You need the following files to flash the Tasmota firmware to the ESP8266 NodeMCU or ESP-01.
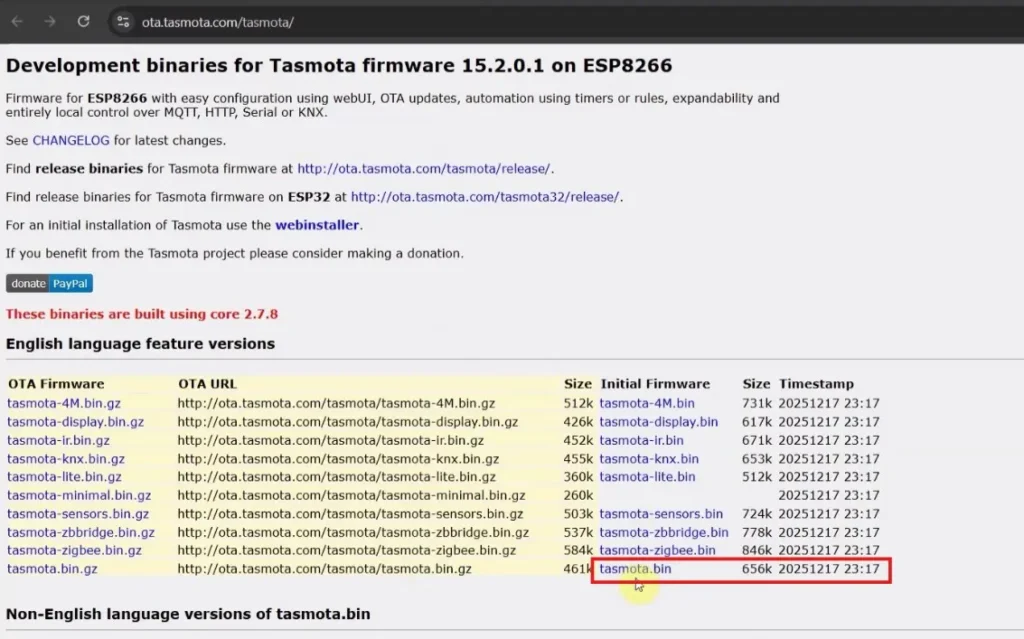
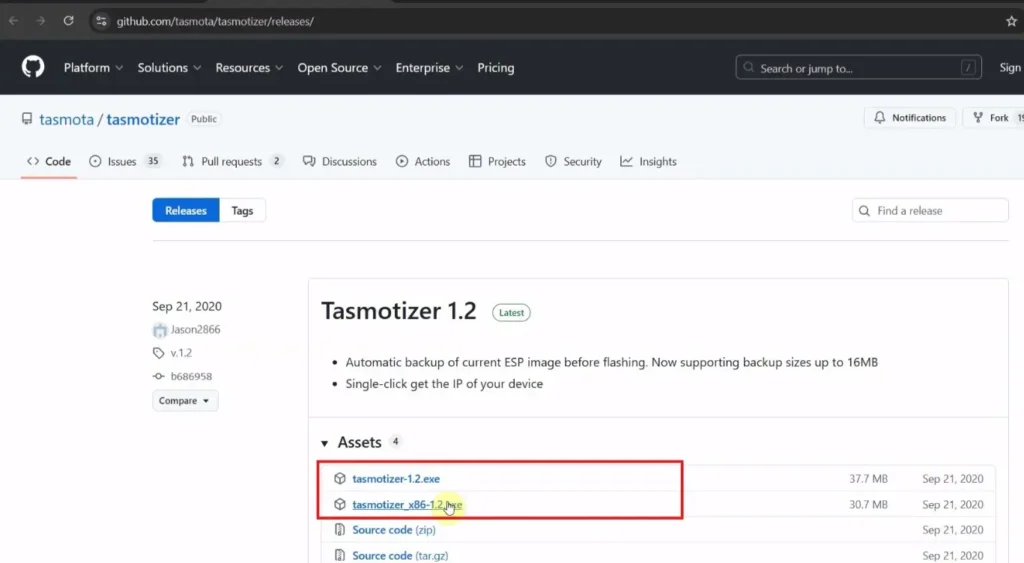
Here, I have used the tasmota.bin firmware for this project. This version supports most common features like relays, LEDs, switches, Alexa, and MQTT.
If you have a 32-bit system, download the tasmotizer_x86-1.2.exe instead of tasmotizer-1.2.exe from GitHub.
No installation is required. Just extract and run the application.
Step 2: Connect ESP8266 to Computer
- Connect your ESP8266 NodeMCU to the computer using a USB cable
- Windows users may need to install CH340 or CP2102 drivers (if the USB port is not detected)
- Note the COM port assigned to your device
Step 3: Open Tasmotizer and Select Port
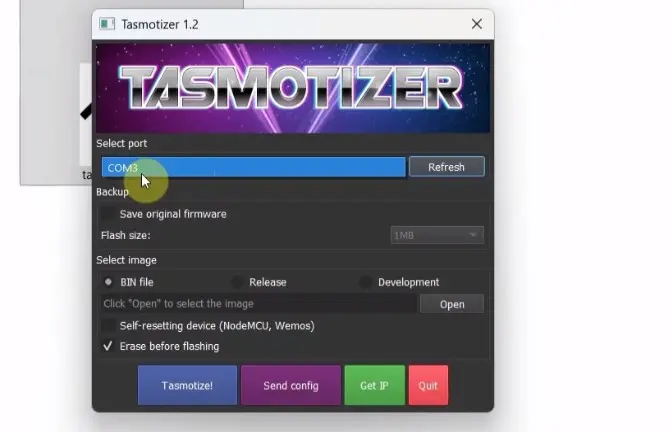
- Open Tasmotizer
- Select the correct COM port
Tasmotizer will now be ready to flash your ESP8266.
Step 4: Select Tasmota Firmware File
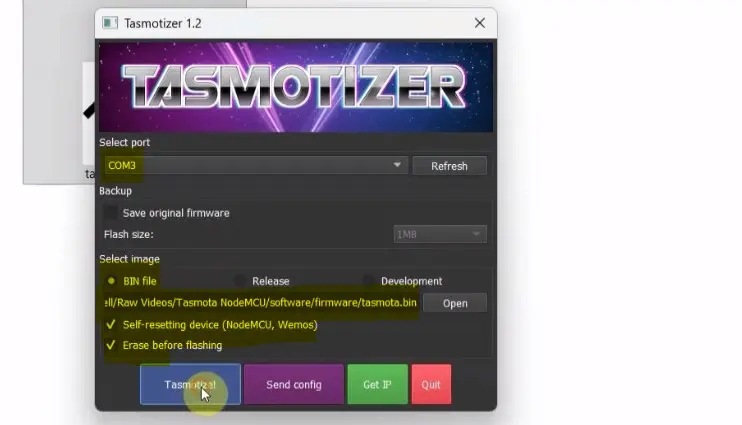
- Select the BIN file.
- Click Open.
- Select the downloaded
tasmota.binfile - Make sure Erase before flashing is checked (recommended)
This ensures a clean installation and avoids old firmware conflicts.
Step 5: Flash Tasmota Firmware
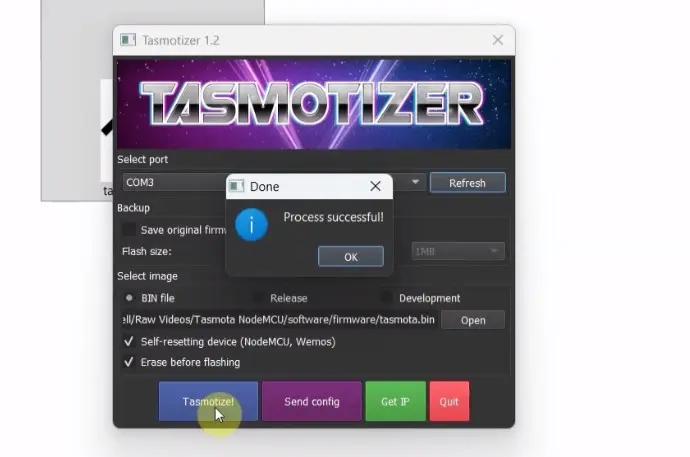
- Click “Tasmotize!”
- Wait for the flashing process to complete
- Do not disconnect the ESP8266 during flashing
Once finished, you will see a success message, and the ESP8266 will reboot automatically.
Step 6: Connect Tasmota to WiFi Network
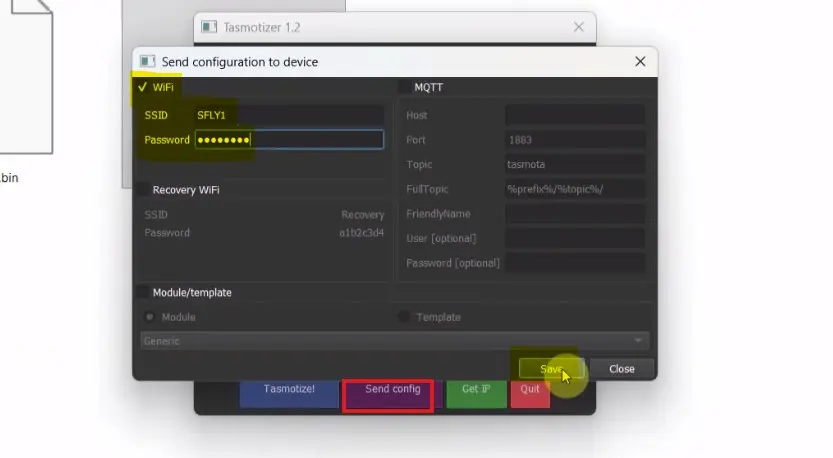
After flashing:
- Click on the “Send config” button.
- Enter your WiFi SSID and password.
- Click Save and wait for 10 seconds.
The device will reboot and connect to your WiFi network.
Step 7: Get the IP to access Tasmota Web Dashboard
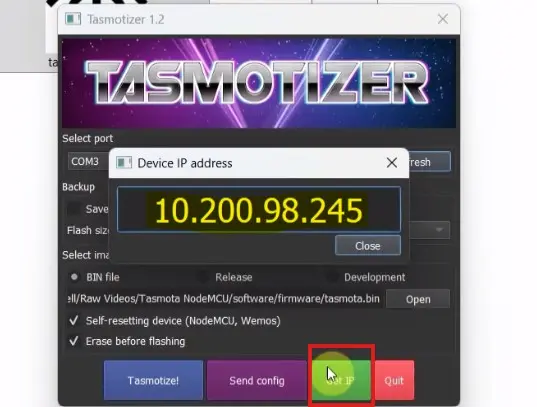
- Click on the “Get IP” button.
- Now copy the IP address.
- Open the IP address in a browser to access the Web Dashboard.
Step 8: Access Tasmota Web Interface
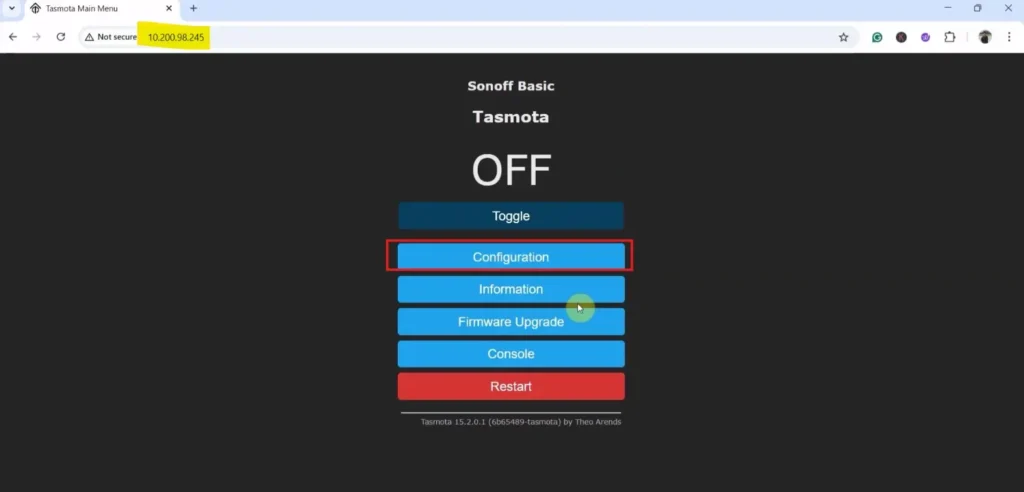
- Open the IP address in a browser to access the Web Dashboard.
You will now see the Tasmota Web Dashboard, where you can:
- Configure GPIO pins
- Control relays
- Set LED indicators
- Enable Alexa integration
- Monitor device status
Configure the ESP8266 GPIO in the Tasmota dashboard
Follow these steps to configure the GPIO pins of the ESP8266 in the Tasmota Dashboard.
Step 1: Select the Module Type:

Click on “Configuration“.
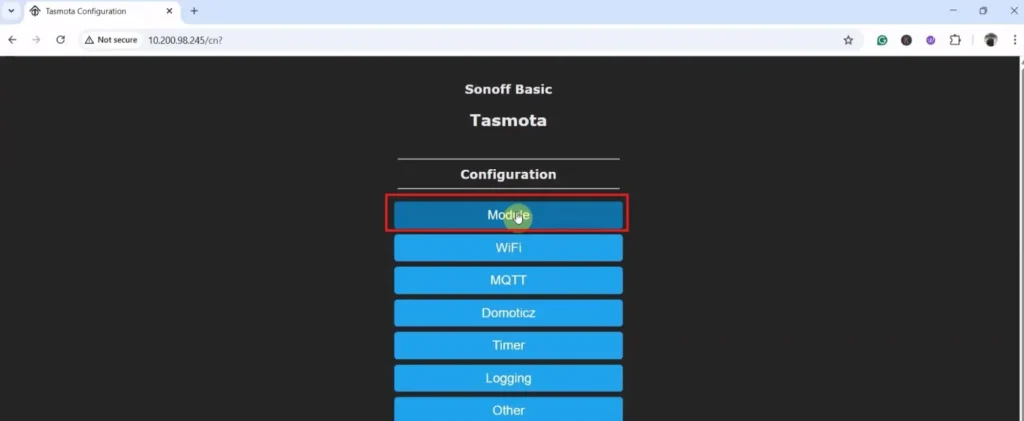
Click on “Module“.
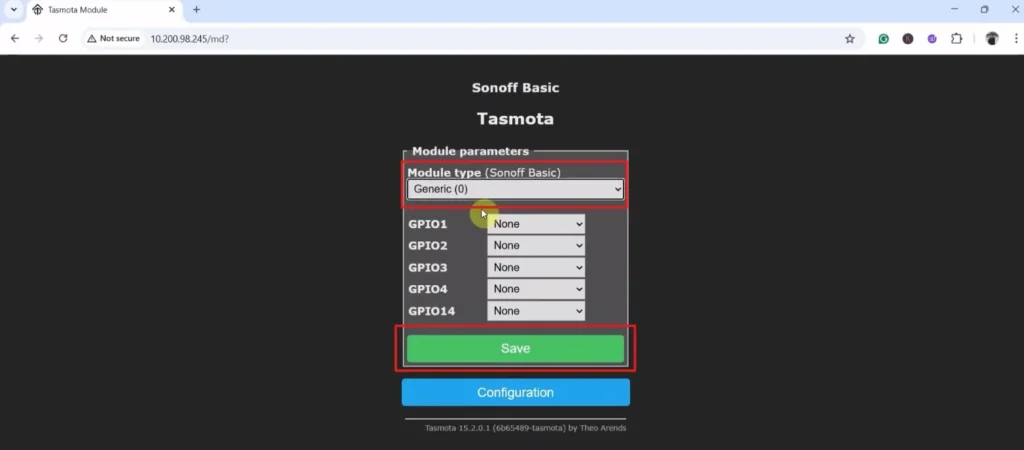
From the drop-down list, select “Generic (0)“.
Click on “Save“.
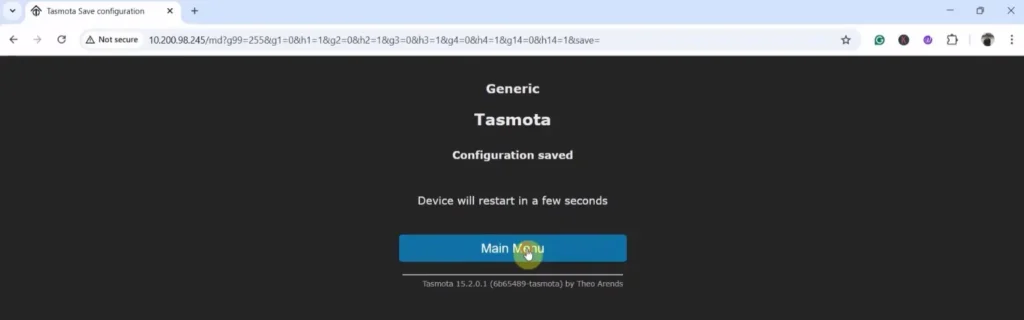
Click on “Main Menu”.
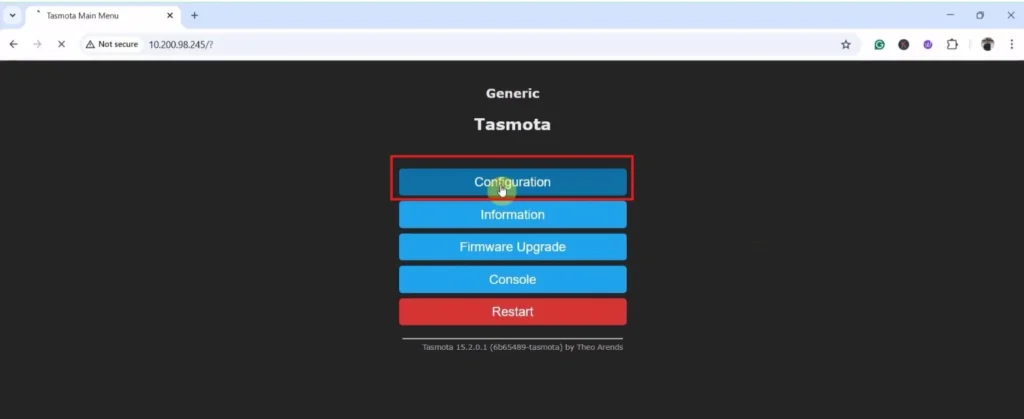
Again click on “Configuration“.
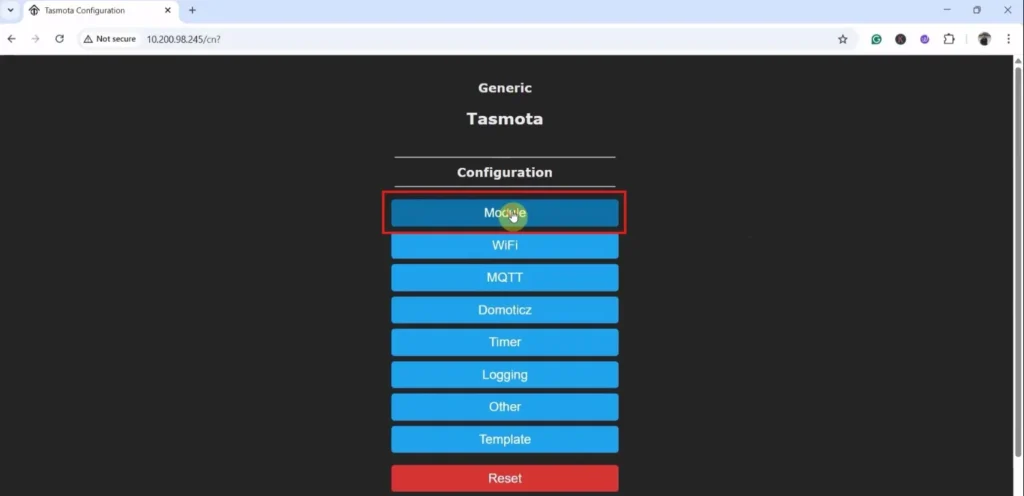
Again, click on “Module“.
Step 2: Configure the GPIO pins in Tasmota Dashboard
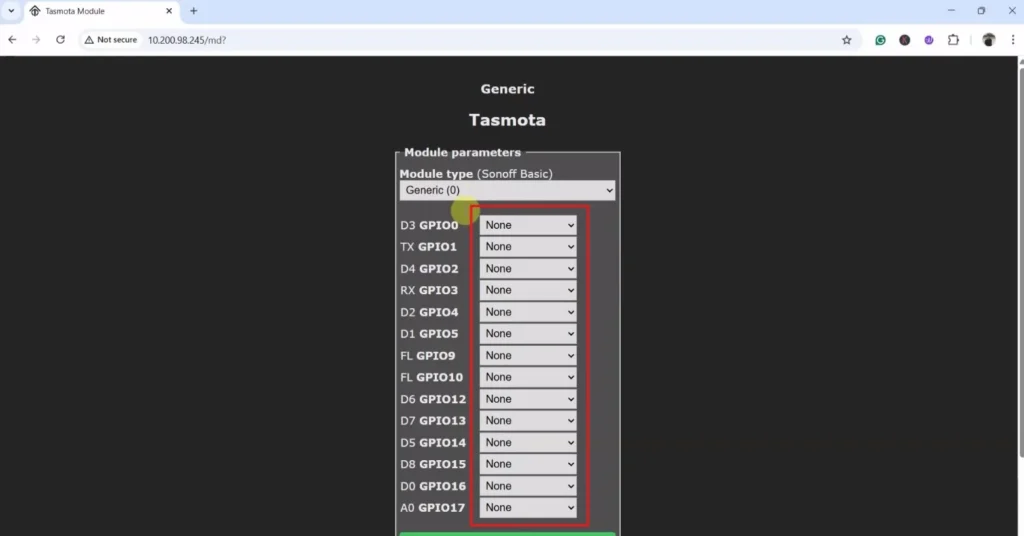
Now you have to configure the GPIO pin connected to the relays, switches, or sensors according to the circuit.
In the circuit, if you use an active-LOW (Relay will turn on for LOW signal at control pin) relay module, then you have to select “Relay_i” for the GPIO pins connected with Relay. For the active-HIGH relay, select only “Relay“.
If you use push buttons (momentary switch), then select “Button” for all the GPIO connected with push buttons. But if you use switch (latched), then select “Switch“.
For the indicator LED, select “Led“.
You also have to select the number to map each switch with the respective relay.
The following picture is just for reference only.
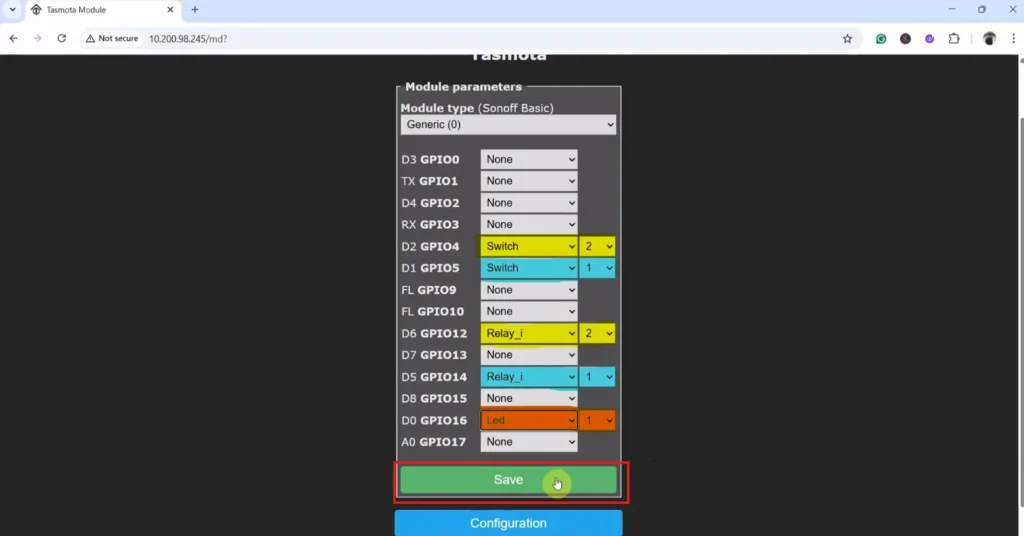
Here the Relay-1 is connected with D5 (GPIO-14), and Switch-1 is connected with D1 (GPIO-5).
After configuring the GPIO pins, click on “Save“.
Click on “Main Menu“.
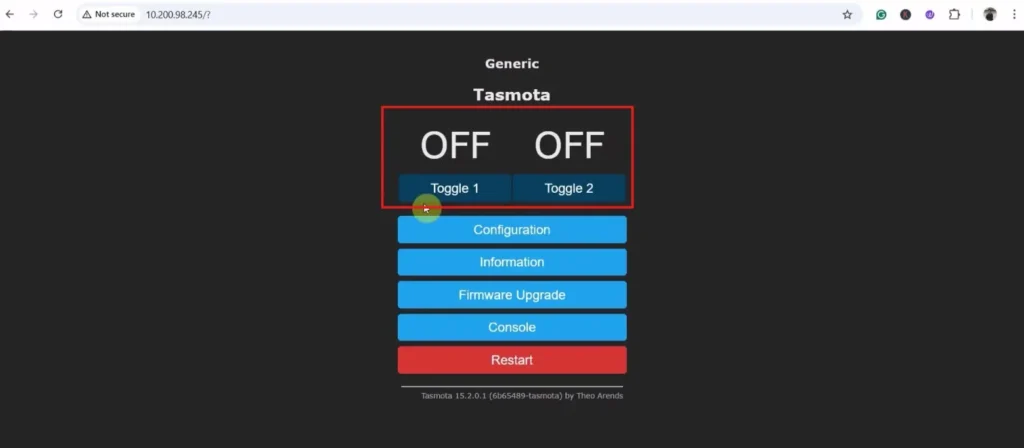
Now the Tasmota web dashboard is ready.
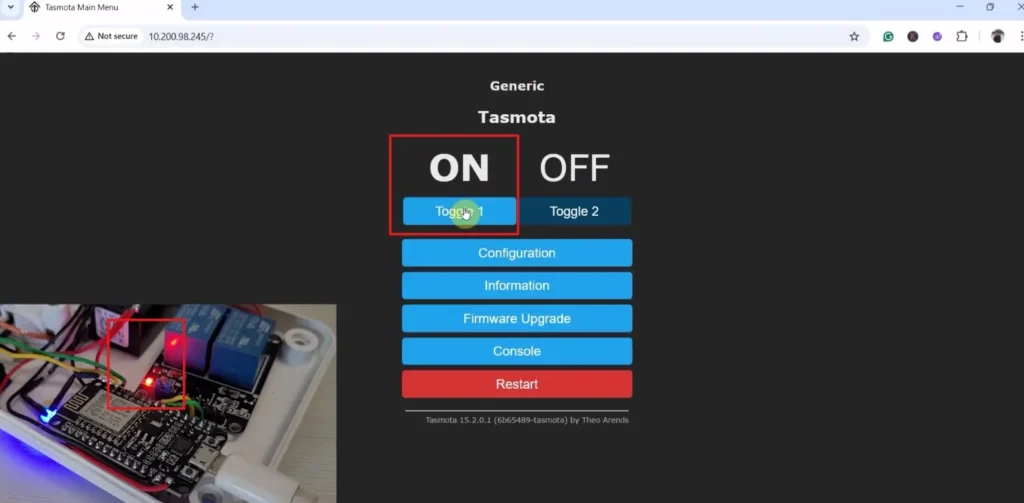
You can control the relays and monitor feedback on the web dashboard.
PCBWay – Professional PCB Assembly Services
PCBWay offers fast, high-quality PCB assembly with lead times starting from 24 hours. Choose from Turn-key, Partial Turn-key, or Consigned options to match your project requirements.

You can also participate in the PCBWay Mascot 3D Printing Design Contest
- PCBWay’s first-ever 3D Printing Design Contest
- Open to all 3D printing enthusiasts
- Design either PCBWay mascot “Eon” or your own original character

- Eon-Themed Design: Create variations of PCBWay mascot Eon (poses, outfits, styles)
- Open Creative Design: Any original 3D character, figurine, doll, anime, mecha, etc.
- Upload the project on PCBWay Open Source Community
- Select CNC & 3D Printing category
- Mention Eon Theme or Open Creative
- Add title, description & required files
- Click Submit
Common Problems and Fixes
ESP8266 not detected
- Use a proper data USB cable
- Install USB drivers (install CH340 or CP2102 drivers)
Flashing fails
- Enable “Erase before flashing”
- Try lower baud rate (57600)
No getting IP for Tasmota dashboard after flash
- Power reset the board
- Wait 30 seconds
Conclusion
Installing Tasmota using Tasmotizer is one of the easiest and safest methods for beginners. With its simple interface and offline capability, Tasmotizer makes flashing ESP8266 devices fast and reliable. Once installed, you can build DIY smart plugs, Alexa-controlled devices, and complete home automation systems—all without writing code.
Click here to find more smart home projects with Tasmota.